Batter Links: Your Gateway to Trending News
Stay updated with the latest trends and insights from around the world.
Fairness in Code: When Smart Contracts Go Rogue
Uncover the hidden risks of smart contracts! Explore how code can go rogue and what it means for fairness in the digital age.
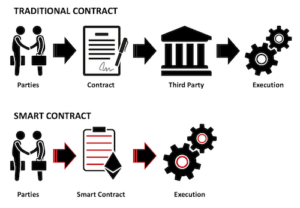
Understanding Smart Contract Failures: What Happens When Code Misbehaves?
Understanding Smart Contract Failures is critical for anyone involved in the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology. These self-executing contracts are designed to facilitate, verify, and enforce the terms of an agreement automatically. However, code misbehaving can lead to significant failures, often resulting in substantial financial losses. Common reasons for these failures include unexpected bugs, incorrect logic, and vulnerabilities that can be exploited by malicious actors. As such, developers must prioritize rigorous testing and audits to mitigate these risks before deployment.
When a smart contract fails, the repercussions can be severe. For instance, if a contract is poorly coded and lacks proper security measures, it could be manipulated, leading to unauthorized fund transfers or loss of user assets. Furthermore, once a smart contract is live on the blockchain, reversing transactions is nearly impossible, emphasizing the need for thorough due diligence and best practices in coding. Blockchain users and developers alike must educate themselves on these risks to navigate the complex landscape of decentralized applications effectively.
Counter-Strike is a popular first-person shooter game that pits two teams against each other, typically terrorists and counter-terrorists. Players can choose to engage in various game modes, including bomb defusal and hostage rescue, utilizing teamwork and strategy. For those looking to enhance their gaming experience, using a bc.game promo code can offer exciting rewards and bonuses that elevate gameplay.
The Importance of Fairness in Smart Contracts: Lessons from Notable Failures
Smart contracts are lauded for their ability to automate and enforce agreements without the need for intermediaries. However, several notable failures highlight the critical importance of fairness in these protocols. For instance, the infamous DAO hack in 2016 led to a loss of over $50 million worth of Ether due to vulnerabilities in the contract's code. These issues stemmed from a lack of clear definitions and safeguards that should ensure fairness in the execution of the contract. Developers must learn from such failures to ensure that the interests of all parties are adequately protected, thereby enhancing trust in decentralized platforms.
The lessons learned from these failures underscore the need for fairness mechanisms within smart contracts. This includes rigorous testing, transparent governance structures, and community oversight to prevent abuse and exploitation. As blockchain technology continues to evolve, integrating principles of fairness will not only help avert disastrous outcomes but will also promote greater adoption of smart contracts across various industries. By prioritizing fairness, developers can build more resilient and equitable systems that serve the interests of all stakeholders involved.
How to Design Fair and Secure Smart Contracts: Best Practices and Common Pitfalls
Designing fair and secure smart contracts is essential to ensure the integrity of blockchain applications. Start by implementing best practices such as thorough requirement gathering, which involves all stakeholders in the process. It is crucial to utilize formal verification methods to mathematically prove the correctness of your contract's logic. Incorporate extensive unit testing and establish a comprehensive audit process involving third-party experts to identify vulnerabilities from the outset. Additionally, document your code meticulously, as well-structured documentation can help others understand its functionality and purpose.
Despite following best practices, developers often face common pitfalls when designing smart contracts. One prevalent issue is the lack of upgradability, meaning that once a contract is deployed, it cannot be changed without significant risk. Ensure that you include an upgrade mechanism or a proxy contract to allow for future adjustments. Another trap is neglecting to handle exceptions and errors properly; always implement robust error handling to avoid unexpected behavior. Finally, take care to manage your contract's gas consumption effectively, as overly complex contracts can lead to high transaction fees and deter users from interacting with your application.